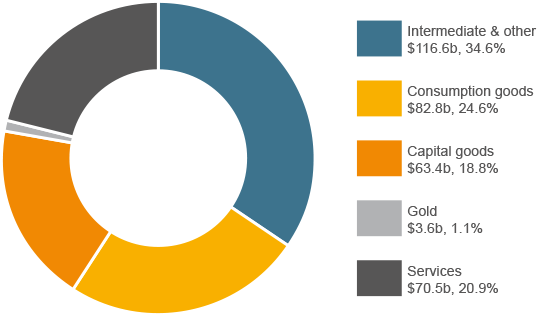Australia's trade in goods and services reached a new high in 2014. Two-way trade grew by 2.4 per cent to $663.8 billion, up from $648.5 billion in 2013. Nearly half of Australia's exports came from minerals and fuels, especially iron ore and coal.
China, Japan, the United States, the Republic of Korea and Singapore were Australia's top five trading partners again in 2014. Over 70 per cent of Australia's trade was with member economies of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum. In 2014, Australia was the 22nd largest exporting country, and the 22nd largest importing country in the world.
Australia has nine Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) currently in force and signed an additional agreement in 2015 with China which will enter into force once domestic processes are complete. Negotiations on the Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement (TPP) successfully concluded in October 2015.
Australia's trade with our aid partners
In 2014, Australia's two-way merchandise trade with countries with which Australia has an ongoing bilateral development partnership was valued at $35.1 billion. In the last 10 years (since 2004) two-way trade has increased by 74.2 per cent. Australia's exports to our development partners have grown by 71.6 per cent while imports have grown by 76.7 per cent in the same period.
Market access for Least Developed Countries*
Australia has provided Least Developed Countries (LDCs) full duty-free and quota-free access to our markets since 2003. This has contributed to notable increases in LDC exports to Australia (averaging 16.2 per cent per year between 2004 and 2014).
* Afghanistan, Angola, Bangladesh, Benin, Bhutan, Burkina Faso, Burma, Burundi, Cambodia, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Haiti, Kiribati, Laos, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Nepal, Niger, Rwanda, Samoa, Sao Tome & Principe, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Solomon Islands, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan (including Former Sudan), Tanzania, Timor-Leste, Togo, Tuvalu, Uganda, Vanuatu, Yemen and Zambia.
By Sector – Australia's Exports
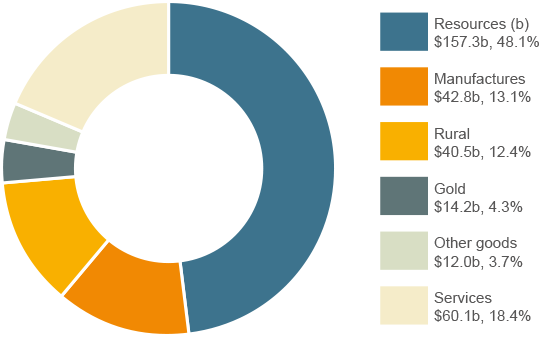
In 2014 Australia's total goods and services exports reached $326.9 billion, an increase of 2.5 per cent from $319.0 billion in 2013. Export volumes grew 6.7 per cent while prices fell 3.7 per cent.
Most export sectors saw a rise in 2014: Rural exports rose 6.9 per cent (or $2.6 billion); Minerals and fuels remained steady (at $157.3 billion); Manufactures increased 4.5 per cent (or $1.9 billion); Other goods fell 3.9 per cent (or $487 million) and Services went up 8.3 per cent (or $4.6 billion).
Exports of goods and services 2014 (a)
Share by sector
(a) Balance of payments basis.
Based on ABS catalogue 5302.0.
By Sector – Australia's Imports
Imports are an important part of Australia's economic prosperity. They help maintain a robust, competitive economy and improve choice for consumers.
Australia's total goods and services imports increased from $329.5 billion in 2013 to $337.0 billion in 2014. Import volumes fell 1.7 per cent while prices rose 4.2 per cent.
Imports of Consumption goods rose 5.2 per cent (or $4.1 billion); Capital goods fell 2.5 per cent (or $1.6 billion); Intermediate & other goods rose 5.5 per cent (or $6.0 billion) and imports of Services fell 0.1 per cent (or $68 million).
Imports of goods and services 2014 (a)
Share by sector
(a) Balance of payments basis.
Based on ABS catalogue 5302.0.