Trade and investment topics
International organisations
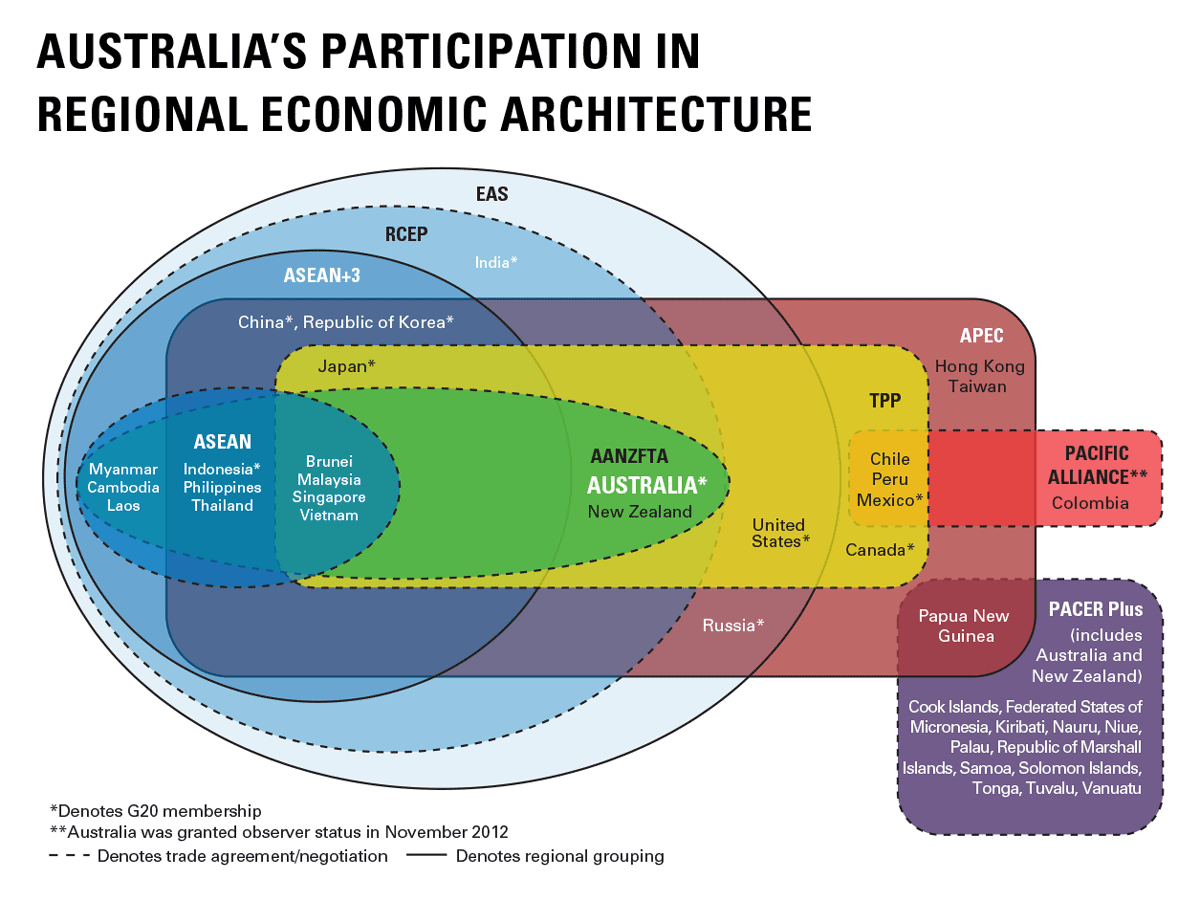
Australia's participation in regional economic architecture
Download this diagram: Australia's participation in regional economic architecture [PDF 550 KB]
This Venn diagram uses a series of overlapping and intersecting circles to demonstrate the relationships and overlapping memberships of the various East Asian and Asia-Pacific regional groupings. This diagram does not show Australia's bilateral Free Trade Agreements.
- ASEAN
- ASEAN (the Association of Southeast Asian Nations) was established in 1967 to accelerate economic growth and social progress in South-East Asia and to promote regional peace and stability. The ten ASEAN Member States are Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam.
- AANZFTA
- The Agreement Establishing the ASEAN-Australia-New Zealand Free Trade Area (AANZFTA) is a comprehensive FTA between the 10 ASEAN Member States, Australia and New Zealand. The agreement entered into force in 2010.
- ASEAN+3
- ASEAN+3 (ASEAN Plus Three) is a forum that functions as a coordinator of cooperation between ASEAN and China, Japan and the Republic of Korea. The first ASEAN+3 Leaders' meeting was held in 1997.
- RCEP
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) negotiations involve the ten ASEAN Member States and ASEAN's six FTA partners – Australia, China, India, Japan, Republic of Korea and New Zealand. The RCEP negotiations were launched by Leaders on 20 November 2012.
- EAS
- The East Asia Summit (EAS) is a regional leaders' forum for strategic dialogue and cooperation on key challenges facing the East Asian region. Membership of the EAS comprises the ten ASEAN Member States, Australia, China, India, Japan, the Republic of Korea, New Zealand, the United States and Russia.
- TPP
- Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement (TPP) negotiations concluded in October 2015. The 12 countries that negotiated the TPP - Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, the United States and Vietnam – represent around 40 per cent of the global economy. In addition to the 12 countries that undertook the negotiations, TPP membership will be open to other Asia-Pacific economies.
- APEC
- The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum was established in 1989. Its primary purpose is to facilitate economic growth and prosperity in the region. APEC currently encompasses 21 member economies.
- PACER Plus
- The Pacific Agreement on Closer Economic Relations (PACER) Plus negotiations were launched by Pacific Islands Forum Leaders in mid-2009.
- Pacific Alliance
- The Pacific Alliance was formed in 2011, and aims to deepen integration between Peru, Chile, Mexico and Colombia, including in the free movement of goods, services, capital and people. Australia was granted observer status to the group in November 2012.
- G20
- The Group of Twenty (G20) is the premier forum for international economic cooperation and decision-making, with members from 19 countries plus the European Union.